|
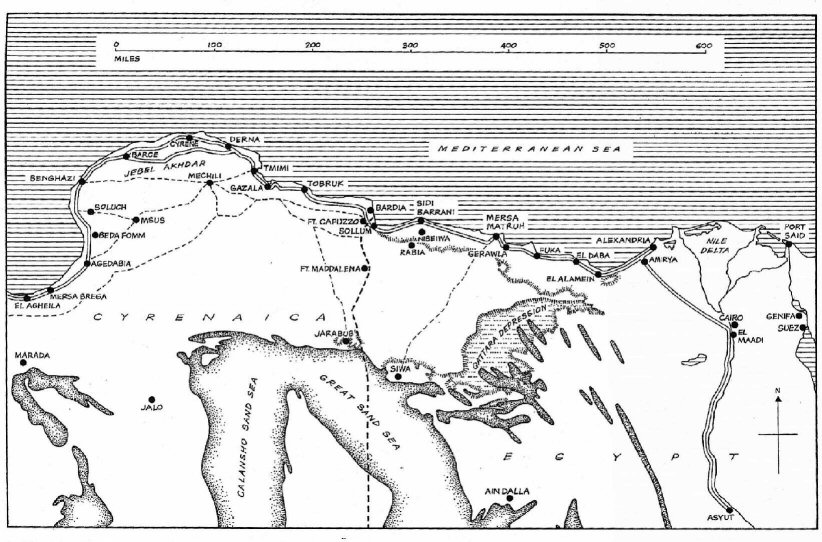
September 13, 1940
The
Italian 10th Army, consisting of six infantry
divisions and 200 tanks, attacks from Libya into
Egypt against the British 4th Indian Division and
the 7th Armored Brigade. The Italians drive 60
miles against token resistance, then halt and set up fortified camps near Sid Barrani.
December 9, 1940 - February 7, 1941
(Operation Compass)
A British
five day raid develops into a major offensive which pushes the
Italians back 500
miles, taking 130,000 prisoners and destroying the
Italian 10th Army. The British stop at El Agheila.
Operation Compass
February 12, 1941
Rommel and
the Germans begin to arrive in Libya. The 5th
Light Division is completely arrived by March 11.
The 15th Panzer is available in May.
April, 1941 (Operation Sonnenblume)
Rommel
attacks the British and drives them back 500 miles.
Tobruk is isolated but does not fall as the tough
Australians refuse to yield. Axis attempts to
take Tobruk on April 14 and April 30 are both
repulsed.
Start of Rommel's Offensive
Siege of Tobruk
May 15, 1941 (Operation Brevity)
The British launch a small-scale counterattack in an
attempt to relieve the isolated garrison at Tobruk.
Halfaya Pass is captured
and Ft. Capuzza and Sollum are held for part of a day but the offensive fails to reach Tobruk.
Operation
Brevity
May 26, 1941 (Operation Skorpion)
Rommel launches an offensive that retakes Halfaya Pass.
Operation Skorpion
June 15, 1941 (Operation Battleaxe)
The British launch a large counterattack in another attempt to
relieve Tobruk. The attack is stopped cold.
Operation Battleaxe
November, 1941 (Operation Crusader)
In a major
offensive, the newly created British 8th Army pushes
Rommel all the way back to his starting point at
Mersa el Braga. Tobruk is relieved after a seige of
242 days. The Italians lose half their army and the
Germans lose a quarter of theirs.
Operation
Crusader
January 21, 1942
The Germans refit
and Rommel counterattacks, driving the British back.
May 26 to June 21, 1942 (Battle of
Gazala)
Rommel attacks the Allied line just west of Tobruk.
The Allies are heavily defeated and forced to
retreat. Tobruk falls on June 21 with a loss
of 35,000 prisoners. Rommel is promoted to
Field Marshal and advances toward Alexandria, Cairo
and the Suez canal with the British making a last
stand at El Alamein.
Operation
Venezia
July 1, 1942 (1st Battle of El Alamein)
Rommel attacks the British
line at El Alamein but the Brits hold.
September, 1942 (Battle of Alam Halfa)
Rommel attempts to
flank the British position but is halted by the
Brits again under their new commander, Montgomery.
October 24, 1942 (Battle of El Alamein)
Battle of El Alamein
Montgomery
launches a major assault against the remnants of the Afrika Korps. The Germans are pushed back for
good.
November
8, 1942 (Torch Landings)
American and
British forces land in French North Africa and
eventually help drive the Axis completely out of
North Africa. The last of the Axis surrender
on May 13, 1943 |